
When it comes to network troubleshooting, security analysis, or performance monitoring, a packet sniffer (also known as a network analyzer or packet capture tool) is an invaluable tool. It allows you to capture, inspect, and analyze data packets that traverse your network, providing insights into everything from traffic flow to network security issues.
In this guide, we’ll explore how to use a free packet sniffer, why it’s useful, and step-by-step instructions for setting up and using one. We’ll also introduce you to some of the best free packet sniffing tools available and explain how to leverage them effectively.
What is a Packet Sniffer?
A packet sniffer is a software tool or hardware device that monitors network traffic and captures data packets as they travel across a network. Packets are small chunks of data that are transmitted over the network, and each packet contains useful information like source and destination addresses, data type, size, and protocol.
Packet sniffers are often used by:
- Network administrators to troubleshoot network issues
- Security professionals to monitor for unauthorized or malicious traffic
- Developers to debug applications by inspecting the traffic
- Penetration testers to perform network security assessments
In essence, a packet sniffer can help you understand what’s going on in your network, from performance bottlenecks to security vulnerabilities.
How Do Packet Sniffers Work?
As discussed above, when a sender transmits data packets, the packets pass through several nodes in a network. Each network adapter and the connected device examines a packet’s control information to see what node the packet is headed toward. Under normal circumstances, if a node finds the packet is addressed to some other node, it drops or ignores the packet. However, in packet sniffing, certain nodes are programmed to not follow this standard practice and collect all or a defined sample of packets, irrespective of their destination address. The packet sniffers use these packets for the analysis of a network.
Depending on who’s using the packet sniffers, it can have both positive and negative use cases. Threat actors can extract critical information from unencrypted messages. Many times users logging into websites over unencrypted transmission expose their credentials (user ids, passwords, etc.) in plain text, which can be easily intercepted by packet sniffers. However, packet sniffing also offers many benefits we’ll discuss later in
Why Use a Packet Sniffer?
There are many reasons you might want to use a packet sniffer, whether you’re troubleshooting a network issue or ensuring the integrity of your data:
1. Troubleshooting Network Issues
By capturing packets, you can analyze network traffic to diagnose performance issues like high latency, dropped packets, or congestion.
2. Monitoring for Security Vulnerabilities
Packet sniffers are essential for identifying unusual or unauthorized traffic, including malware communications, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, or data exfiltration attempts.
3. Debugging Application Problems
Packet sniffers allow developers to inspect traffic between clients and servers, helping them debug issues related to protocols, payloads, and data transmission.
4. Optimizing Network Performance
By analyzing packet traffic, network administrators can identify bandwidth hogs, optimize traffic flow, and improve overall network efficiency.
5. Educational Purposes
Packet sniffing is an excellent way to learn about networking protocols, the OSI model, and the internal workings of network communication.
Types of Packet Sniffers
There are two major types of packet sniffers:
Hardware Packet Sniffers
As the name suggests, it’s a hardware component plugged into a network for packet sniffing or network analysis purposes. Hardware packet sniffers are commonly used when network administrators have to analyze or monitor a particular segment of a large network. With a physical connection, these packet sniffers allow administrators to ensure all packets are captured without any loss due to routing, filtering, or any other network issue. A hardware packet sniffer can have the facility to store the packets, or they can be programmed to forward all captured packers to a centralized location for further analysis.
Software Packet Sniffers
Software Packet Sniffers are the more common type of packet sniffers used by many organizations. Every computer or node connects to the network using a Network Interface Card (NIC), which is generally configured to ignore the packets not addressed to it. However, a Software Packet Sniffer changes this behavior, so one can receive every bit of network traffic for analysis. The NIC configuration is known as promiscuous mode. The amount of information collected depends on whether the packet sniffer is set on filtered or unfiltered mode.
Depending on the size and complexity of a network, multiple packet sniffers might be required to monitor and analyze a network effectively. This is because a network adapter can only collect traffic from one side of a switch or a router. Similarly, in wireless networks, most network adapters can connect to only a single channel at a given time. To capture packets from other channels, one has to install multiple packet sniffers.
Best Free Packet Sniffer Tools
Several free packet sniffing tools are available for use, each offering varying levels of complexity, features, and compatibility. Below are some of the best free packet sniffers that you can use:
1. Wireshark
Wireshark is the most popular and widely-used packet sniffer. It’s an open-source, cross-platform tool that allows you to capture and interactively browse traffic on a computer network. Wireshark supports a vast range of protocols, making it highly versatile.
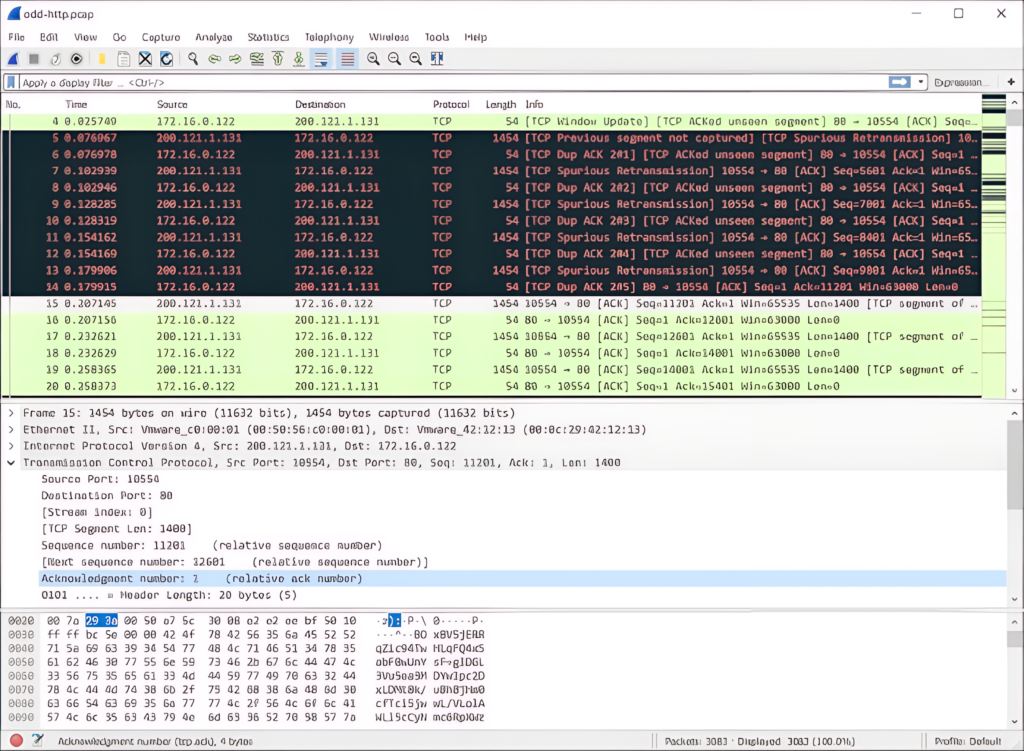
- Key Features:
- Supports hundreds of protocols.
- Real-time packet capture and analysis.
- Detailed filtering and search options.
- Export captured data for further analysis.
- Graphical interface for easy navigation.
- Why Use Wireshark?
- It’s highly customizable, providing in-depth network traffic analysis.
- Excellent for both beginners and advanced users due to its user-friendly interface and advanced features.
How to Use Wireshark:
- Download and Install: Go to the Wireshark download page, choose your operating system, and install it.
- Select Your Network Interface: Open Wireshark and select the network interface you want to capture packets from (e.g., Ethernet or Wi-Fi).
- Start Capturing: Click the “Start capturing packets” button (the shark fin icon). Wireshark will begin capturing packets in real time.
- Filter Packets: To find specific traffic, use the filter bar. For example, type
httpto capture only HTTP traffic. - Stop Capturing: When you have enough data, click the red stop button to end the capture.
- Analyze the Data: You can examine packet details like protocol, source, destination, and data payloads. Use color coding for easy identification of different types of packets.
2. tcpdump
tcpdump is a command-line network packet analyzer that comes pre-installed on many Unix-based operating systems (including Linux and macOS). It provides powerful packet sniffing capabilities and is widely used by system administrators and network engineers.
- Key Features:
- Command-line tool that allows for deep customization.
- Can capture traffic for specific interfaces, protocols, or IP addresses.
- Saves captured data to a file for later analysis.
- Filters traffic based on source, destination, protocol, etc.
- Why Use tcpdump?
- Lightweight and powerful for those comfortable with the command line.
- Ideal for users with scripting and automation needs.
How to Use tcpdump:
- Install tcpdump: On Linux, you can install it using the command
sudo apt-get install tcpdump(on Ubuntu). On macOS, tcpdump is often pre-installed. - Basic Packet Capture: Run
sudo tcpdumpto start capturing packets on the default network interface. - Capture on Specific Interfaces: To capture on a specific interface, use
sudo tcpdump -i eth0. - Apply Filters: Capture specific traffic like HTTP packets with
sudo tcpdump -i eth0 port 80. - Save Captures: To save the captured data to a file for later review, use
sudo tcpdump -i eth0 -w capture.pcap. - Review Captures: Open the saved
.pcapfile with Wireshark or another tool for detailed analysis.
3. Nmap
Nmap is primarily known as a network scanning tool, but it also has packet sniffing capabilities, particularly through its Nmap Scripting Engine. Nmap can help capture and analyze packets related to network discovery and security testing.
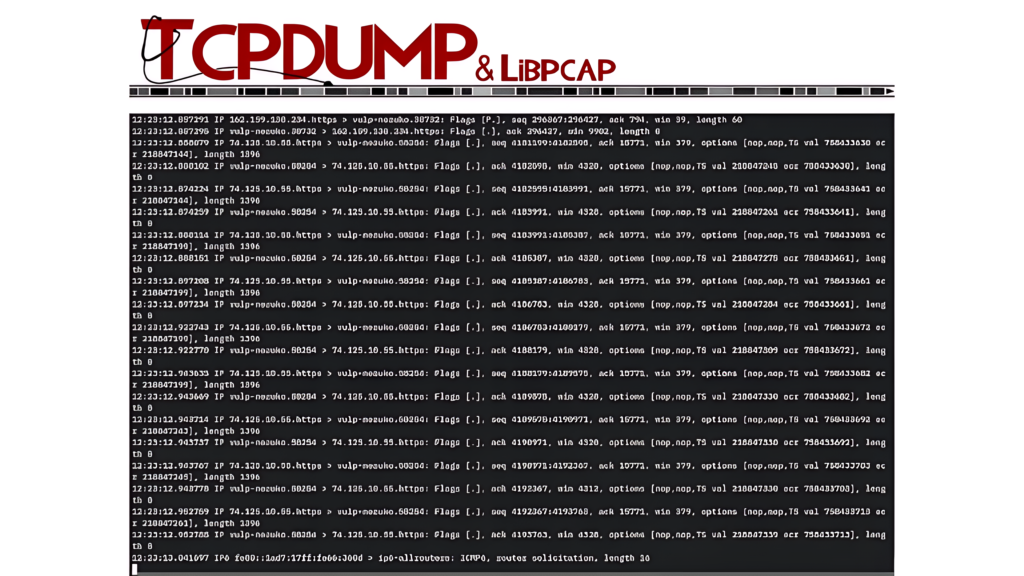
- Key Features:
- Network discovery and vulnerability scanning.
- Supports packet sniffing and analysis through scripts.
- Runs on various operating systems, including Linux, Windows, and macOS.
- Why Use Nmap?
- Ideal for network penetration testing and security analysis.
- Can be used to gather information about services, open ports, and host availability.
How to Use Nmap:
- Install Nmap: Install Nmap via your package manager (e.g.,
sudo apt install nmapon Linux) or download it from the official Nmap website. - Run Basic Network Scan: Use
sudo nmap -sn 192.168.1.0/24to scan your local network for live hosts. - Capture Specific Traffic: Use Nmap’s packet sniffing options to capture traffic by running
sudo nmap -sP -n 192.168.1.1. - Examine Results: Analyze the results using Nmap’s built-in scripting engine to gain insights into the network.
4. SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor
SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor is an advanced network monitoring tool allowing you to monitor availability and security parameters with intelligent mapping, pre-configured dashboards, and advanced alerting features. With its network packet sniffer, you can get to the root cause of network issues and troubleshoot errors quickly. The tool identifies more than 1,200 applications, which makes it easier to analyze traffic and identify what’s leading to a poor end-user experience. It allows you to calculate response times for different applications, along with their data volume, and other performance indicators to categorize the traffic into different types and risk levels. You can use the Quality of Experience dashboard to get a holistic view of several metrics related to the network and application performance.
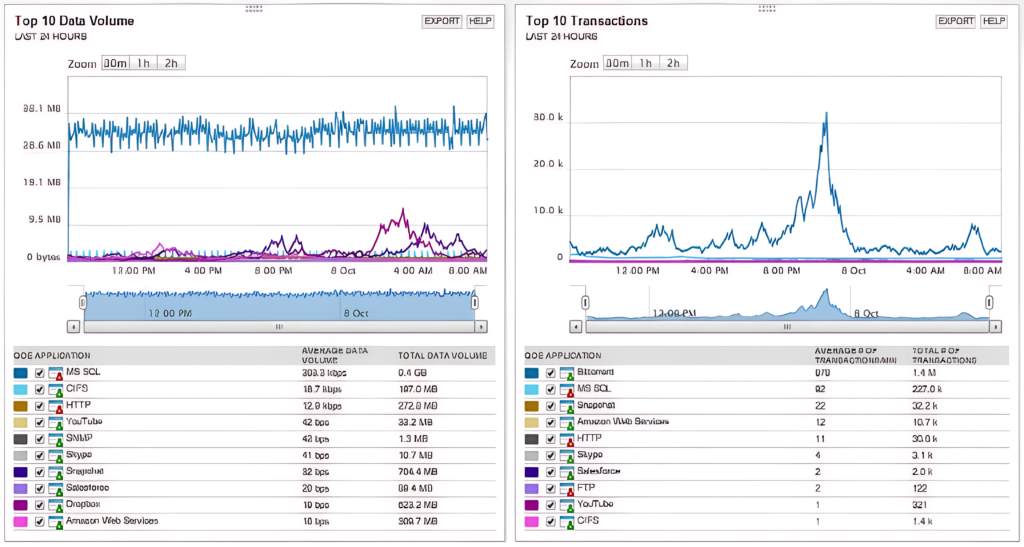
- Key Features:
- Real-time performance metrics
- Automatic device discovery
- Intelligent alerts
- Issue diagnosis and root cause analysis
- Network maps
- Customizable dashboards
- Natural scalability
- Why Use Microsoft Network Monitor?
- An understanding of NPM is important for network professionals who are responsible for achieving the level of network performance needed for today’s enterprise. That’s why it’s no surprise that the global network performance monitoring market is projected to reach $4.2 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 7.1% from 2022 to 2031.
How to Use Microsoft Network Monitor:
Engineers use network monitoring to prevent and troubleshoot network outages and failures. In this article, we’ll describe how network monitoring works, its primary use cases, the typical challenges related to effective network monitoring, and the main features to look for in a network monitoring tool.
Top 5 Benefits of Packet Sniffing
- Detecting the Root Cause of a Network Issue
- Troubleshooting Network Issues
- Traffic Analysis
- Bandwidth Management
- Network Security and Compliance.
1. Detecting the Root Cause of a Network Issue
Today, in most enterprise networks, there are several user groups and applications, along with a complex mix of legacy and next-gen networking equipment. Ensuring all applications and servers perform without any performance bottlenecks is a huge undertaking. When an application or a service experiences an issue, it can be a difficult task to identify which network or application component is responsible for the slowdown. This is why network administrators monitor their network continuously for routine maintenance and optimization. With packet sniffers, they can collect information from all points of their network to quickly identify the components responsible for latency, jitters, or packet loss.
2. Troubleshooting Network Issues
Whenever IT teams receive tickets related to network connectivity, they can perform PCAP analysis to measure the response times or latency in a network. It helps in determining the amount of time a packet takes to travel from a sender to a receiver. With this analysis, teams can identify congested links, detect the applications generating an unusual amount of traffic, and take remedial actions to resolve the issue. Using modern Wi-Fi packet sniffers, teams can get performance metrics for different access points and wireless controllers. Many advanced network monitoring tools offer additional features for fault, performance, and network availability monitoring. It’s also possible to correlate network data across the stack and perform hop-by-hop network path analysis to troubleshoot network issues and minimize network downtime.
3. Traffic Analysis
IT teams can also collect the packet data for predictive analysis. They can visualize this data to detect the peaks and troughs in network demand over longer periods. Using advanced IP sniffers and packet analyzers, they can categorize the data based on destination server IP addresses, ports involved in communication, the volume of traffic, and more. With all this analysis, it’s possible to distinguish critical traffic (required for VOIP, ERP suites, CRMs, etc.) from non-business traffic (social media, unauthorized messengers, etc.). Also, IT administrators can filter and flag suspicious content.
4. Bandwidth Management
Slow or intermittent networks can significantly impact business productivity and lead to huge losses. Businesses rely on advanced network monitoring tools to avoid such issues. However, most of these tools also rely on packet sniffing to analyze the traffic in a network. Packet sniffers help in preventing the misuse of the network by both internal and external users. As discussed above, with traffic analysis, IT teams can easily identify the traffic flow and WAN bandwidth utilization, any irregular increase in network usage, and more. Equipped with this data, they can prioritize bandwidth allocation for mission-critical applications, and even restrict certain applications.
5. Network Security and Compliance
It’s not rare for threat actors to infiltrate an enterprise network and compromise sensitive data. However, their activities can also remain hidden for a long period, and many times they use advanced malware to make malicious use of enterprise resources. Regular traffic analysis allows the detection of any suspicious increase in outbound traffic flow. Packet sniffers help in detecting a surge in traffic, attempts at network intrusion, and enable deeper evaluation and mitigation of security threats. They help in checking the status of WAN and endpoint security systems. Packet sniffers also help in regulatory compliance documentation by logging all of the perimeter and endpoint traffic. Moreover, with packet sniffers, security teams can verify the effectiveness of their security setup consisting of several firewalls, web filters, WAF, IPS/IDS systems,