In the modern world of IT infrastructure, virtualization has become a cornerstone of efficient resource management, scalability, and flexibility. VMware ESXi is one of the most widely used solutions for server virtualization, but what exactly is ESXi, and why should you consider using it in your environment?
What is VMware ESXi?
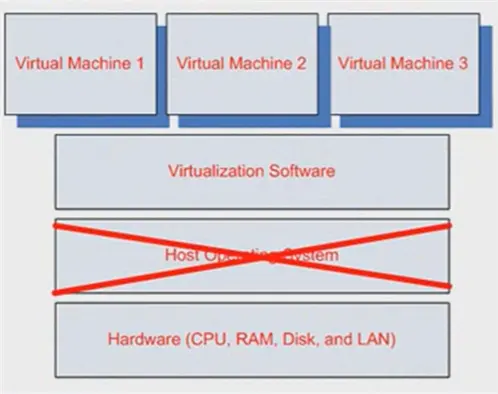
VMware ESXi is a bare-metal hypervisor developed by VMware, which allows you to run multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server. It’s part of VMware’s vSphere suite of products and is designed to efficiently virtualize hardware resources, making them available to virtualized operating systems.
Key Features of VMware ESXi:
- Bare-metal Hypervisor: Unlike Type 2 hypervisors that run on top of an existing operating system, ESXi runs directly on the physical hardware, eliminating the need for a host OS. This results in better performance and more efficient use of hardware resources.
- Minimalistic Design: ESXi has a very small footprint compared to other hypervisors, with its core operating system being around 150MB in size. This makes it very efficient and optimized for virtualization.
- Centralized Management: VMware ESXi can be managed using vCenter Server or vSphere Client, enabling centralized management of virtual environments.
- High Availability and Fault Tolerance: ESXi supports features like vMotion (migration of VMs across hosts), HA (High Availability), and FT (Fault Tolerance) to ensure continuous uptime and resilience.
- Resource Allocation: VMware ESXi provides tools to allocate CPU, memory, storage, and networking resources to virtual machines, enabling fine-grained control over how resources are distributed across multiple workloads.

How Does VMware ESXi Work?
VMware ESXi is a type of hypervisor used for creating and managing virtual machines (VMs) on physical servers. It is part of VMware’s virtualization platform, which allows users to run multiple virtualized operating systems (OS) on a single physical machine, known as the host machine.
ESXi is considered a bare-metal hypervisor, meaning it runs directly on the physical hardware (the host system) without the need for an underlying operating system. This contrasts with a hosted hypervisor, which runs on top of an existing operating system.
Key Components of VMware ESXi:
- VMware ESXi Hypervisor:
- The hypervisor is the core of ESXi and is responsible for managing all virtual machines (VMs) and their interaction with the physical hardware of the host server.
- It directly interacts with the underlying hardware (CPU, memory, storage, etc.) to allocate resources to the VMs.
- ESXi is a lightweight hypervisor, as it has a very small footprint compared to traditional operating systems. It does not require a full operating system, which helps minimize resource usage and improve performance.
- VMkernel:
- The VMkernel is a specialized kernel that runs as part of ESXi and provides the core functionality of the hypervisor. It manages key tasks like memory management, CPU scheduling, I/O handling, and network communication for the virtual machines.
- The VMkernel also interacts with the underlying hardware and provides services like virtual disk management and virtual network configuration for the VMs.
- Virtual Machines (VMs):
- ESXi runs multiple virtual machines on a single physical host. Each VM behaves as an independent system with its own virtual CPU, memory, disk, and network interface.
- VMs run their own guest operating systems (Windows, Linux, etc.) and applications, which are isolated from each other and from the host machine.
- Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM):
- The VMM is responsible for managing the execution of virtual machines. It ensures that each VM gets the appropriate amount of resources from the host machine and manages tasks like scheduling CPU time for VMs and providing access to virtualized hardware.
- Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL):
- The HAL abstracts the physical hardware from the virtual machines. This allows ESXi to provide each VM with virtualized hardware resources (such as CPU, memory, and storage), making it possible to run multiple different operating systems on the same physical host.
How ESXi Allocates Resources:
- CPU Scheduling:
- ESXi allocates CPU resources to virtual machines based on their demands and configured resource limits. The VMkernel manages CPU scheduling by dividing the CPU time into time slices for each virtual machine.
- It uses techniques like CPU affinity and shares to prioritize the allocation of CPU resources among VMs.
- Memory Management:
- ESXi uses memory overcommitment, which allows VMs to use more virtual memory than is physically available. It does this by using techniques like transparent page sharing (TPS) and ballooning to optimize memory allocation.
- The balloon driver within the guest operating system helps ESXi reclaim memory by giving control back to the VMkernel when the host is running low on physical memory.
- Storage:
- ESXi supports various storage options, such as local storage, iSCSI, Fibre Channel, and Network-Attached Storage (NAS).
- It uses datastores to organize and manage storage resources, and each VM’s virtual disk is stored within a datastore.
- VMware’s VMFS (Virtual Machine File System) is commonly used for managing virtual disks and ensures that virtual machine data can be read and written efficiently.
- Networking:
- ESXi provides virtualized network interfaces through vSwitches (virtual switches). These vSwitches enable communication between VMs and with external networks.
- ESXi also supports vSphere Distributed Switches (vDS), which allow for more advanced networking features such as centralized network management and consistent policies across multiple hosts in a cluster.
Virtualization Workflow in ESXi:
- Installation of ESXi:
- ESXi is installed directly onto a physical server. Once installed, it operates independently, with no need for an underlying operating system. The server’s hardware is abstracted and managed by the ESXi hypervisor.
- Creation of Virtual Machines:
- Through vSphere Client (a web-based or desktop interface), administrators can create and manage VMs. Each VM gets a specified amount of CPU, memory, disk space, and network connectivity.
- Virtual Machine Operation:
- Once the VM is created, ESXi assigns it the necessary virtual hardware resources and launches the operating system inside the VM. The VM behaves like a regular physical server, but it’s running inside the ESXi hypervisor.
- The VM interacts with the virtual hardware, and any requests for physical resources (CPU, memory, etc.) are mediated by the VMkernel.
- Management and Monitoring:
- Administrators can use VMware vCenter Server to manage multiple ESXi hosts from a centralized interface. This allows for more advanced features like VM migration (vMotion), load balancing (DRS), and high availability (HA).
- ESXi also integrates with tools like vSphere HA and vSphere FT (Fault Tolerance) to ensure that VMs remain available even in the event of hardware failures.
Why Do You Need VMware ESXi?
There are several reasons why organizations and individuals choose to use VMware ESXi for virtualization. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Server Virtualization
ESXi allows you to run multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server, which significantly optimizes hardware utilization and reduces the need for additional physical servers. This results in cost savings related to hardware, power, and cooling.
2. Isolation and Security
Each virtual machine on ESXi is isolated from others, meaning that issues in one VM (e.g., crashes, malware) won’t affect others on the same host. This is particularly important for businesses needing secure environments for multiple applications or services.
3. High Availability and Fault Tolerance
VMware ESXi supports high-availability (HA) features, where VMs can automatically restart on other hosts in the case of hardware failure, minimizing downtime. It also offers fault tolerance (FT) to ensure continuous availability for mission-critical applications.
4. Centralized Management
With ESXi, you can manage multiple virtual machines through a centralized platform like VMware vCenter. This simplifies tasks like provisioning, monitoring, and maintenance, improving efficiency in large-scale virtualized environments.
5. Resource Allocation and Optimization
ESXi allows you to allocate CPU, memory, and storage resources to VMs dynamically. It ensures that resources are optimized for performance based on workload demands. You can even prioritize resource allocation for more critical VMs.
6. Cost Efficiency
Virtualizing with ESXi means you can consolidate workloads onto fewer physical servers, reducing hardware costs, space requirements, and operational expenses (such as power and cooling).
7. Support for Various Operating Systems
ESXi supports a wide range of operating systems, including Linux, Windows, and other versions of Unix. This makes it a versatile solution for companies using diverse software environments.
8. Scalability
ESXi can scale from small to large environments, providing flexibility as your infrastructure grows. VMware also offers features like Distributed Resource Scheduling (DRS) and Storage DRS to balance workloads efficiently.
9. Integration with VMware Ecosystem
VMware ESXi integrates seamlessly with other VMware products, such as VMware vSphere, VMware vSAN (for storage), and VMware NSX (for networking). This allows for a more robust and feature-rich virtualized infrastructure.
10. Cost-Effective Licensing
While VMware ESXi offers a free version with basic features, there are also paid versions with additional enterprise-grade features like vCenter integration, vMotion, and enhanced backup and recovery options.
Cost-Effective Solution for Virtualization
VMware ESXi is considered a cost-effective solution for virtualization for several reasons, especially when compared to the expenses of maintaining a large number of physical servers. Here’s how it helps reduce costs:
1. Reduced Hardware Costs
By running multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server, VMware ESXi allows you to maximize the use of your existing hardware. Instead of purchasing multiple servers for each workload or application, you can consolidate workloads onto fewer, more powerful machines. This results in significant savings on physical hardware purchases.
2. Lower Operational Costs
With fewer physical servers to manage, companies save on the ongoing costs of maintaining and operating hardware, such as:
- Power consumption: Fewer physical servers mean less electricity usage for powering and cooling the hardware.
- Cooling: Data centers and server rooms can be expensive to cool, so reducing the number of physical machines lowers air-conditioning and cooling costs.
- Rack space: Virtualization minimizes the need for large server racks, freeing up space and reducing the cost of physical infrastructure.
3. Free Version of ESXi
VMware offers a free version of ESXi, which includes basic features for virtualization. While the free version lacks advanced features like centralized management (vCenter), high availability, or fault tolerance, it’s a great option for smaller businesses or testing environments. For companies on tight budgets, this provides a low-cost entry point into server virtualization.
4. Improved Resource Utilization
VMware ESXi optimizes resource allocation by enabling multiple VMs to share resources (CPU, memory, and storage) on a single physical server. This leads to better resource utilization and reduces the need to over-provision hardware, as you can dynamically allocate resources as needed based on workload demands.

5. Simplified IT Management
VMware’s centralized management tools, such as vCenter Server, help administrators manage all virtual machines and resources from a single interface. This reduces the administrative overhead associated with maintaining and configuring individual physical servers. With automation features like VM provisioning, patching, and resource management, IT teams can focus on higher-value tasks rather than routine hardware management.
6. Consolidation of Workloads
ESXi enables organizations to consolidate workloads, which can reduce the number of separate systems that need to be supported. Instead of managing different servers for different tasks (e.g., one server for a web application, another for a database), you can virtualize these workloads, running them on fewer physical machines. This reduces administrative time and lowers costs associated with supporting a diverse IT infrastructure.
7. Licensing Flexibility
VMware offers various licensing models, so organizations can choose the one that best fits their needs and budget. You can start with the free version of ESXi and later upgrade to more feature-rich versions if your business grows, enabling you to scale and add more advanced functionality without having to replace the underlying infrastructure.
8. Disaster Recovery Savings
Virtualization also simplifies disaster recovery (DR). Since virtual machines can be easily backed up, moved, and restored, companies can save on the infrastructure and costs associated with traditional disaster recovery setups. VMware’s capabilities like vMotion allow virtual machines to be moved between hosts with minimal downtime, reducing the need for expensive dedicated disaster recovery hardware.
9. Reduced Software Licensing Costs
Running virtual environments with VMware ESXi can also help optimize software licensing costs. Many software vendors offer reduced or flexible pricing for virtualized environments, especially if the virtual machines are running on a shared infrastructure. Additionally, by consolidating workloads, companies may be able to reduce the number of operating system licenses or application licenses they need.
10. Easier Testing and Development
ESXi makes it cost-effective for organizations to set up test environments by virtualizing applications, operating systems, and development environments. Developers can spin up multiple VMs to test applications or software without needing dedicated physical machines, significantly reducing the cost of setting up and maintaining testing environments.